Dram Memory Slot (x2) Function
Posted : admin On 3/28/2022DDR RAM or DDR SDRAM is a type of computer memory. It stands for: Double Data Rate Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory. So what does that mean?
- Dram Memory Slot (x2) Functions
- Dram Memory Slot (x2) Function Tool
- Dram Memory Slot (x2) Function Chart
Dynamic Random Access Memory stands for DRAM or Dynamic RAM which is the more common memory found in a computer. The reason its synchronous dynamic RAM is because the RAM is synchronized with the processor. The Double Data Rate is self-explanatory it just means that the RAM transfers twice as much data as the SDR (single data rate) SDRAM does.
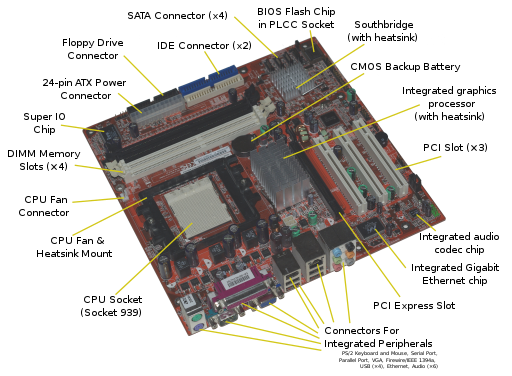
How can you tell the difference between DDR SDRAM and the other types of RAM such as SDR SDRAM and DDR2 SDRAM? Well DDR SDRAM has only one notch (slightly more to one side) and it differs from DDR2 RAM because it is a wider notch and they are not in the same spot. What this means is that the memory slots in the motherboard must have one notch so that the DDR RAM can fit into it. The picture below demonstrates that.
DDR Specifications
DDR RAM (Double Data Rate) which means it can transfer double the data without increasing the clock speed. Typical clock speeds were 100Mhz, 133Mhz, 166Mhz and 200MHz.
Dram Memory Slot (x2) Functions
Megabyte (MB) and Gigabytes (GB) measure the size of DDR SD-RAM. They vary in size from 128mb-1Gb. The common sizes are 256mb, 512mb and 1Gb. DDR2 RAM and DDR3 RAM have both increased the speed and size even further and they are similar prices so if possible go for DDR2 or DDR3.

Dram Memory Slot (x2) Function Tool
Related Articles
The concept of memory rank applies to all memory module form factors, though in general it tends to matter primarily on server platforms, due to the larger amounts of memory they manage. A memory rank is a block or area of data that is created using some, or all, of the memory chips on a module. A rank is a data block that is 64 bits wide. In dynamic RAM (DRAM), the most common type of RAM, a transistor and a capacitor pair up to make a memory cell. The capacitor holds a bit of information (in the form of a 1 or 0), while the transistor acts as a switch, allowing the control circuitry to change the state of the memory.
- Memory Slots
Dram Memory Slot (x2) Function Chart
Leave DDR RAM and return to the Homepage